Fabrication of 6FDA-HFBAPP Polyimide Asymmetric Hollow Fiber Membranes and Their CO2/CH4 Separation Properties
Gan C J , Xu X C , Jiang X W
Chinese Journal of Polymer Science, 37 (2019): 815–826. DOI: 10.1007/s10118-019-2255-7
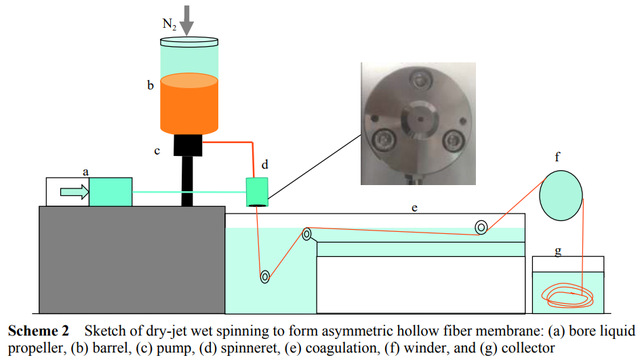
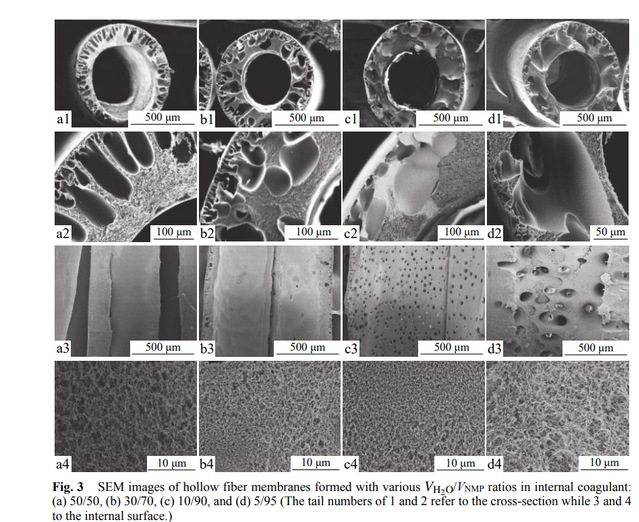
Abstract: In this work, poly(amide acid) solution, the precursor of polyimide, was synthesized by the reaction of 4,4′-(hexafluoroisopropylidene)diphthalicanhydride and 2,2-bis[4-(4-aminophenoxy)phenyl]-hexafluoropropanane in the solvent of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) and tetrahydrofuran (THF). Then, hollow fiber membranes for high flux gas separation were prepared by dry-jet wet spinning using the precursor solution of poly(amide acid) as the spinning dope and a subsequent imidization process. Silicone rubber was further coated outside the obtained hollow fiber membranes to repair the defects on the denser layer. The effects of internal, external coagulation bath ratios with air gap, and coating solution concentrations on the morphologies, structures, and separation performance of the membranes were studied. Results showed that the sponge-like support layer was formed when the content of NMP was increased from 50 % to 90 % in the internal coagulation bath. The outer surface of the membrane became denser when the water content in the external coagulation bath increased from 40 % to 100 %, and the separation coefficient of CO2/CH4 increased by 2 times. This value could reach up to 1.4 when the air gap was 6 cm. With tuning the mass fraction of silicone rubber as 5%, hollow fiber composite membranes with uniform coating layer and an improved separation coefficient of 5.4 could be obtained.