Nano Research Energy发表我课题组通过优化气-固-液三相界面促进可充电锌空气电池/燃料电池性能提升性最新成果
近日,Nano Research Energy (中科院Top 1区, Scite Score 39)发表我课题组在可充电锌空气电池/燃料电池领域最新成果。论文题目为《Hydrophobicity engineering of hierarchically ordered SiO2/Fe-N-C catalyst with optimized triple-phase boundary for boosting oxygen reduction reaction》。
近年来,人们对Fe-N-C单原子催化剂(SACs)赋予了极大关注。然而,Fe元素在热解过程中的迁移和聚集使得高Fe负载和均匀分散原子之间的平衡优化成为一项具有挑战性的工作,最终导致了高度的结构非均质性。此外,由于大多数Fe-Nx活性位点集中在碳载体的微孔中,导致金属位点的不可及性,从而只有4.5%的Fe-Nx位点可用于ORR。如何提高Fe-Nx位点在Fe-N-C SACs中的暴露和利用效率成为关键。
本工作针对上述问题开发了一种由SiO2模板触发的空间限域策略,用于调整 Fe-N-C 催化剂的介孔结构,同时建立疏水边界,从而优化 Fe-N-C 催化剂中 ORR 的气-固-液三相界面从而提高其 ORR 性能。优化后的 SiO2(4)/Fe-N-C 在 0.1 M KOH 中ORR半波电位为 0.886 V。特别经 30,000 次循环后的 E1/2仅损失 32 mV。密度泛函理论(DFT)计算证实,SiO2诱导的碳缺陷对 FeN4中心的电子构型有关键调节作用,优化了氧中间体的吸附能。SiO2(4)/Fe-N-C作为空气阴极直接用于锌-空气电池(ZABs)展现出超过 1013小时的耐久性和444.10 mW cm-2的高率密度,显著优于大多数已报道的无贵金属电催化剂。这项工作为优化用于能源存储应用的单原子催化剂的三相边界提供了一条新途径。
论文第一作者为博士生张杨,论文链接:https://doi.org/10.26599/NRE.2025.9120180
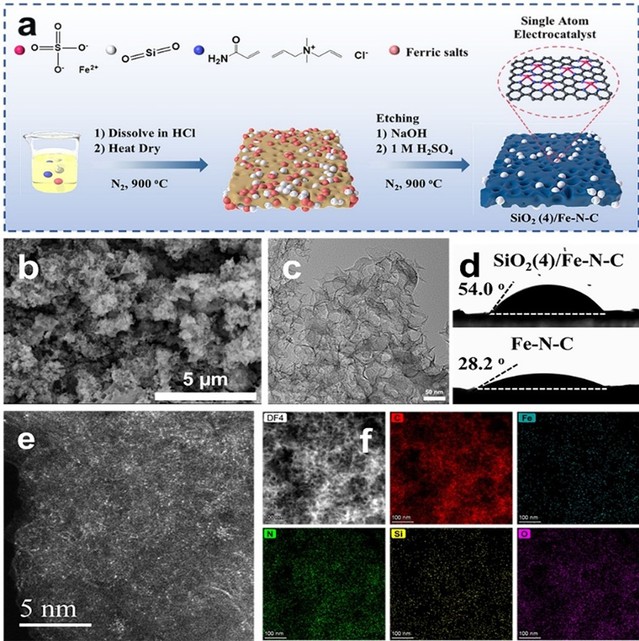
Figure 1 (a) Schematic illustration of the synthesis for SiO2(4)/Fe-N-C. (b) SEM image and (c) TEM image of SiO2(4)/Fe-N-C. (d) Contact angle measurements of SiO2(4)/Fe-N-C and Fe-N-C. (e) AC-HAADF-STEM image of SiO2(4)/Fe-N-C. (f) HAADF-STEM image of SiO2(4)/Fe-N-C and corresponding EDX elemental mappings.
f SiO2(4)/Fe-N-C and Pt/C at 0.7 V (vs. RHE) under a rotating rate of 1600 rpm.
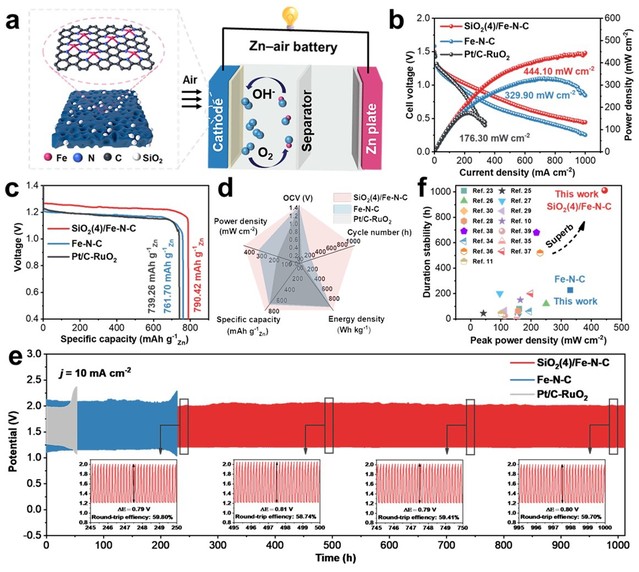
Figure 2 (a) Schematic diagram of assembled rechargeable ZABs. (b) Polarization and corresponding power density curves, (c) discharge specific capacity, (d) a radar map of OCV, power density, specific capacity, energy density and number of cycles and (e) galvanostatic charge-discharge cycling profiles for SiO2(4)/Fe-N-C-, Fe-N-C and Pt/C+RuO2-based ZABs. (f) A comparison of ZABs performance in recently reported works and in this work (Refer to references in the ESM).
